Sunscreen: Everything you need to know!
Published Jul 6, 2021 • By Candice Salomé
With summer vacation approaching, many of us will choose to have some fun in the sun! While spending time outdoors it's important to remember to protect your skin against harmful UVA and UVB rays to avoid sunburn, or worse. However, among the broad variety of sunscreens available on the market, it can be difficult to find the right one.
What type of sunscreen should you use? What is SPF? What is the difference between "waterproof" and "water resistant' sunscreen?
We answer these questions and more!

What is the purpose of sunscreen?
The sun, as pleasant as may be, can be harmful if we do not take proper precautions. Apart from sunburn, it can also cause premature aging of the skin or worse, in the long-term it can cause skin cancer.
Sun protection is essential to avoid the various risks associated with sun exposure.
>> Find out how to protect yourself from skin cancer in our article <<
There for, it's important to create a barrier between your skin and UV (ultraviolet) rays: UVA and UVB.
What is the difference between UVA and UVB rays?
UV radiation is part of the natural energy produced by the sun. On the UV spectrum, UV rays have a shorter wavelength, so they are not visible to the eye. UVA has a wavelength of 400 to 315 nanometers and UVB has a wavelength of 315 to 280 nanometers.
Though your eyes cannot see UVA and UVB, your skin can feel it:
- UVA, with its longer wavelength, penetrates deeply into the dermis and is responsible for skin aging (dark spots, wrinkles, etc.)
- UVB, with its shorter wavelength, penetrates less deeply into the dermis and is responsible for skin burning (sun burn, blisters, the majority of skin cancers).
Sun protection does not in any way prevent you from tanning, in fact the opposite is true. Gradual tanning will last longer than one obtained by repeated sunburns.
What sunscreen should we use?
Sunscreens offer various protection levels, called SPF, ranging from 6 to 50+. It can therefore be difficult to find your way around and choose the right sunscreen.
What is SPF ?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor and can be found on products designed to protect the skin from ultraviolet rays, whether they are sunscreens or certain face creams or beauty products.
The SPF acronym is followed by numbers such as 15, 20, 30 and 50. But what do they mean?
SPF is a measure of how much protection a sunscreen provides against UVB rays, the rays that cause skin damage and sunburn. The SPF values tell you how much sunburn protection it offers. In general, a sunscreen with:
- SPF 15 blocks 93% of UVB rays
- SPF 30 blocks 97% of UVB rays
- SPF 50 blocks 98% of UVB rays.
SPF is calculated by dividing the sun radiation dose needed to cause sunburn with the dose needed to cause sunburn without sunscreen.
SPF = sunburn radiation dose with sunscreen / sunburn radiation dose without sunscreen
So, if it takes 15 times longer for skin to burn with sunscreen on than it does without sunscreen, the SPF would be 15.
There is a common misconception that SPF is related to the time of sun exposure. For example, many believe that if they typically get sunburned in one hour, then a SPF 15 sunblock will allow them to stay in the sun for 15 hours (15 times longer) without getting a sunburn. This is not true because SPF is not related to the time of sun exposure, but to the amount of sun exposure.
A high number SPF does not allow you to spend extra time outdoors without reapplying, this SPF ratio is calculated in ideal conditions (in a laboratory) and does not take into account weather conditions, time of day, skin type, quantity of sunblock applied, how the sunblock is applied, or other environmental or individual factors.
It is therefore recommended to reapply sunscreen as often as possible, minimum every two hours.
What is waterproof sunscreen?
Waterproof sunscreen does actually not exist. Both sweat and water can rinse sunscreen from our skin, so since 2012 the FDA has barred manufacturers from making the claim that sunscreen is "waterproof" or "sweatproof". Some sunscreens however, are water-resistant.
What is water-resistant sunscreen?
For a sunscreen to use the water-resistant designation, the FDA requires that it undergo testing. All sunscreens that are indicated as water-resistant must have a rating of 40 or 80. This rating indicates how long the sunscreen will remain effective (e.g. on your skin) when your skin is wet, either while swimming or sweating. This means that after 40 or 80 minutes of sweating or swimming, you must reapply.
- Sunscreens with a water rating of 40 will be marked "water-resistant".
- Sunscreens with a water rating of 80 will me marked "very water-resistant".
What is broad spectrum sunscreen?
Broad spectrum means that it provides effective protection against both UVA and UVB rays, the solar wavelengths proven to cause skin damage and lead to skin cancer.
How to choose your sunscreen?
The best type of sunscreen is the type that you will continue to purchase and use year after year.
The CDC and the Skin Cancer Foundation both recommend always using a broad spectrum sunscreen with minimum SPF 15 or higher for daily use, and SPF 30 or higher for days with extended periods outdoors or during physical activity.
Sunscreen options come in a variety of types and textures, including lotions, creams, ointments, gels, sprays, and even wax sticks. Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Cream sunscreen is best for dry skin and the face.
- Gel sunscreen is good for areas with a lot of hair, like the scalp or the male chest.
- Sunscreen sticks are helpful and good to use around the eyes and nose.
- Sunscreen sprays are often a convenient choice for parents since they are quick and easy to apply on children. Make sure to use a sufficient amount of these products to protect all exposed skin.
- There are also a number of sunscreen options developed for specific purposes or situations, such as for babies or people with sensitive skin.
To choose the right SPF for you, it can also help to consider the color of your skin, hair and eyes. This allows you to estimate, the reaction your skin has when exposed to the sun. Then, you should take your phototype into consideration, which can help you to determine the appropriate SPF for you.
What is the phototype?
Phototype is another word for skin type. American dermatologist Thomas B. Fitzpatrick created, in 1975, the "Fitzpatrick scale" where he identified 6 phototypes. These 6 phototypes are classified according to the color of the skin, hair and eyes, but also according to the skin's capacity to tan.
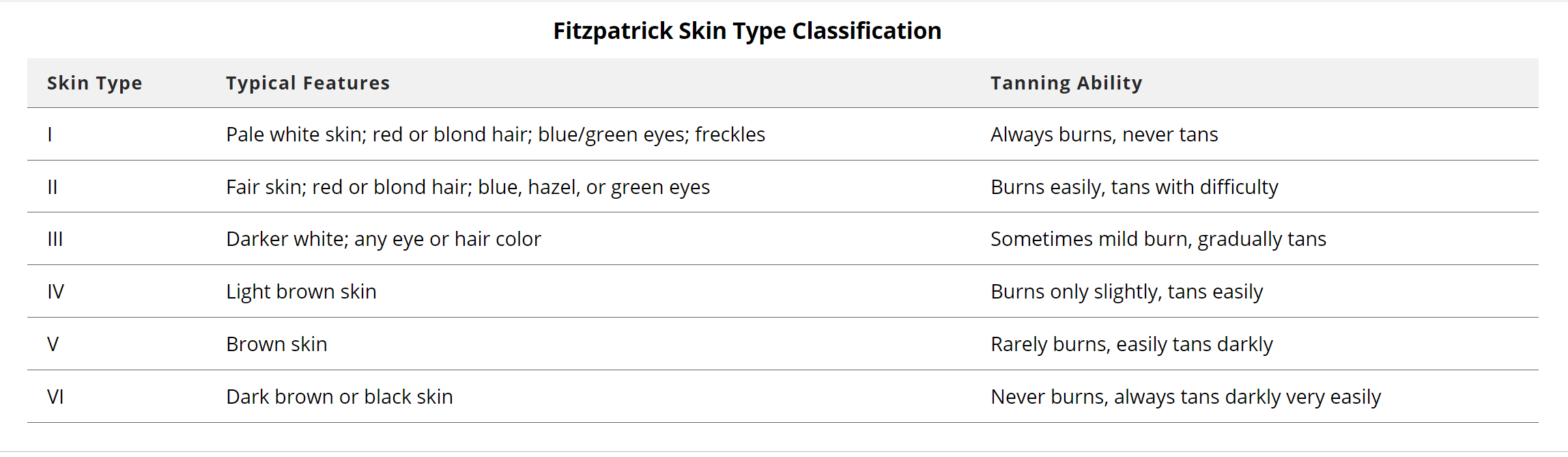 Source: MSD Manual
Source: MSD Manual
So, if you are phototype I or II, it is recommended that you choose an SPF 50 or 50+.
If you are phototype III or IV, it's a good idea to choose an SPF 30-50.
If you are phototype V or VI, you may want to opt for an SPF 15-30.
What is the difference between chemical sunscreen and physical (mineral) sunscreen?
Chemical sunscreens protect you by absorbing UV rays instead of letting them reach the skin and typically contain one or more active ingredients such as oxybenzone or avobenzene. According to experts, chemical sunscreens are undeniably effective and present very few risks. It is recommended to apply them 15 minutes before exposure to the sun.
The only drawback? Their negative impact on our oceans and marine life. Scientists have discovered that some of the chemicals included in sunscreen and other personal care products may threaten the health of coral reefs and other marine life when they wash off of our skin as we swim. Researchers at the National Academy of Sciences are currently working on a study examining the environmental impacts of sunscreen ingredients which is expected to be completed this year.
Because of this, many people are making the switch to physical sunscreens.
Physical sunscreens (also called mineral sunscreen) protect you by deflecting the sun's rays using active ingredients titanium dioxide and/or zinc oxide.
Interested in making the change to a more environmentally responsible sunscreen? The American Academy of Dermatology Association states that as long the mineral sunscreen offers SPF 30 or greater, broad spectrum protection, and water-resistance, it will be effectively protective and it should be safe to use.
Share your thoughts and your questions with the community in the comments below!
Take care!
Sources:
- How to decode sunscreen labels, American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA)
- UV Radiation & Your Skin, The Skin Cancer Foundation
- Fitzpatrick Skin Type Classification, MERCK MANUAL
- Ask the Expert: Does a High SPF Protect My Skin Better?
- How to Read a Sunscreen Label, The Skin Cancer Foundation
- Sunscreen FAQs, AADA
- Sunscreen: How to Help Protect Your Skin from the Sun, FDA
- Which sunscreen should I use?, MedicalNewsToday
- What is Water-Resistant Sunscreen?, HealthCentral
- Skincare Chemicals and Coral Reefs, National Ocean Service, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), U.S. Department of Commerce
- Sun Protection Factor (SPF) and Sunscreen, VeryWellHealth
Comments
You will also like

Spoon theory: What is it and how can it help people living with chronic illness?
Apr 13, 2022 • 8 comments

What is the psychological impact of chronic pain? Carenity members share their experience!
May 27, 2021 • 9 comments

 Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter
